Measure-- provides a quantitative indication of the extent, amount, dimensions, capacity, or size of some attribute of a product or process.
Metric-- a quantitative measure of the degree to which a system, component, or process possesses a given attribute.
Indicator-- a metric or combination of metrics that provide insight into the software process, a software project, or the product itself.
Causes of defects and their origin
| Design | Specification/Requirements | Code |
|
|
|
Size-Oriented Metrics
Size-oriented metrics are derived by normalizing quality and/or productivity measures by considering the "size" of the software that has been produced. (Ex. errors per KLOC, defects per KLOC, cost per KLOC, errors/person-month, etc.)
Function-Oriented Metrics
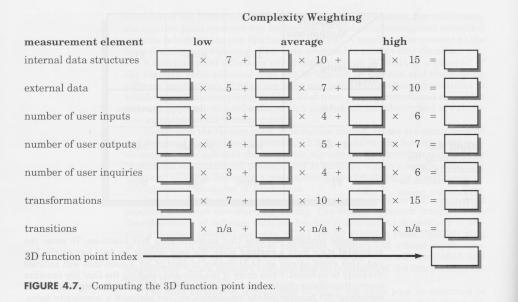
Functionality cannot be directly measured, so it must be derived indirectly using other direct measures. Albrecht suggested a measure called the function point, which is derived using an empirical relationship based on countable measures of software's information domain and assessments of software complexity.

After collecting the above data, a complexity value is associated with each count, and the function points are computed, using the following formula: FP = count-total x [0.65 + 0.01 x (sum)F sub i]
| Programming Language | LOC/FP (average) |
| Assembly Language | 320 |
| C | 128 |
| Cobol | 105 |
| Fortran | 105 |
| Pascal | 90 |
| Ada | 70 |
| Object-oriented languages | 30 |
| Fourth gen. languages (4GL) | 20 |
| Code generators | 15 |
| Spreadsheets | 6 |
| Graphical languages (icons) | 4 |
Function Point Links
Function
Point FAQ
What are function
points?
How are function
points useful?
Auditing function
point counts
PSI - Function point
analysis
Suggested Links for Further Readings
Software Engineering
Laboratory
U.S. Army software
Metric System Web site
List of WWW references for software process
metrics
Last Modified: Wednesday, 6-Jan-1999 9:30:00 CDT
Copyright
© 1997-1999 University of Mississippi. All rights reserved.
Comments: reithel@bus.olemiss.edu